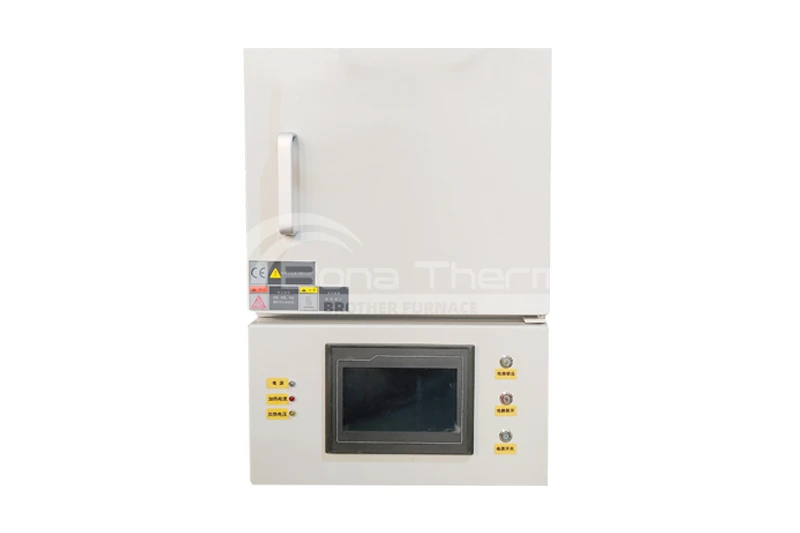
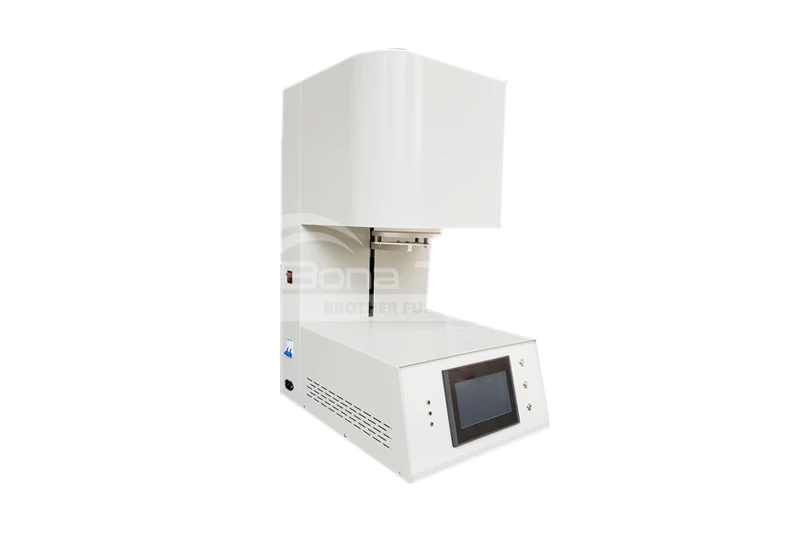
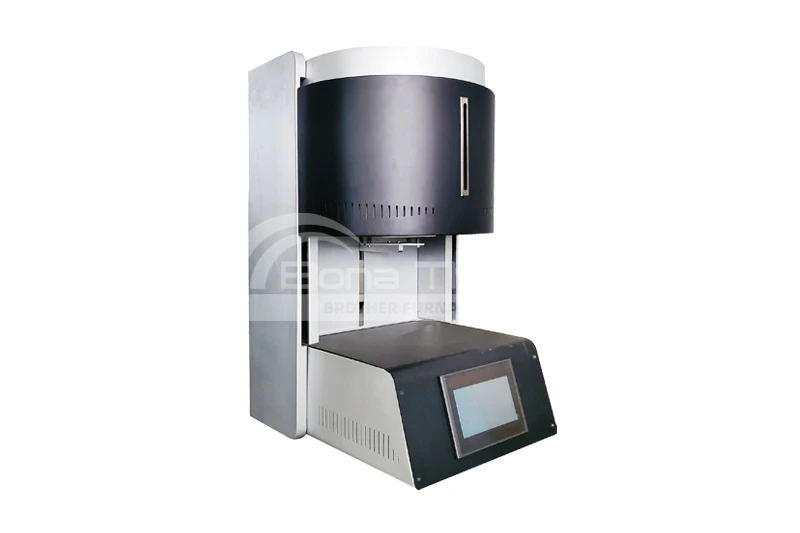
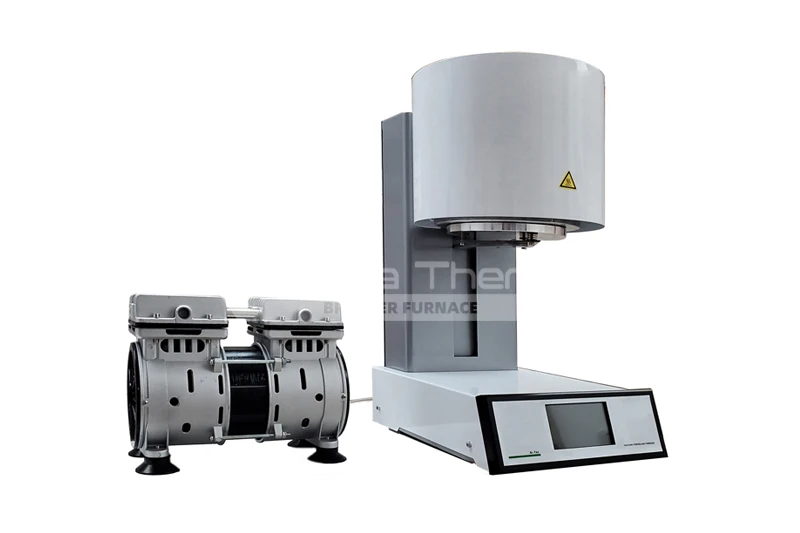
What Materials Can Be Sintered in Dental Furnaces?
Generally, a dental furnace is primarily used for sintering dental prostheses. However, the functionality of a dental furnace is far more versatile than you might think. In addition to dental applications, it can also be used to sinter various other materials. This article will discuss the different materials that can be processed in a dental furnace.

Materials That Can Be Sintered in a Dental Furnace
1. Zirconia
Zirconia is one of the most widely used dental materials, prized for its high strength and excellent aesthetic properties. Zirconia dental prostheses need to be sintered at high temperatures, typically between 1400°C and 1600°C. Through precise sintering processes, zirconia prostheses achieve optimal mechanical performance and biocompatibility, making them ideal for crowns and bridges.
2. Alumina
Alumina dental prostheses also offer good biocompatibility and aesthetic results. It is commonly used in the production of all ceramic crowns and bridges. The sintering process for alumina requires higher temperatures, usually around 1600°C, to ensure the material's strength and translucency.
3. Glass Ceramics
Glass-ceramic materials hold a significant place in dental restorations, especially for anterior teeth. The sintering temperature for glass ceramics generally ranges from 800°C to 900°C. Sintered glass ceramic prostheses exhibit excellent aesthetics and relatively high strength.
4. Metal Ceramics
Metal ceramic dental prostheses combine the strength of metal with the aesthetics of ceramics. Common metal substrates include cobalt-chromium alloys and titanium alloys, covered with a layer of ceramic coating. Metal ceramic prostheses require high-temperature sintering, typically between 800°C and 950°C, to securely bond the ceramic to the metal base.
5. Resin-Based Composites
Resin-based composite materials are primarily used for temporary restorations and specific dental components. These materials require lower sintering temperatures, generally between 200°C and 300°C. Although resin-based composites are not as strong as ceramics, they are easy to process and suitable for short-term use.
6. Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys are favored for their excellent biocompatibility and strength, often used in dental implants. The sintering process for titanium alloys needs to be conducted in a protective atmosphere to prevent oxidation. The typical sintering temperature ranges from 1200°C to 1400°C.
Conclusion
A dental furnace can sinter a variety of materials, including zirconia, alumina, glass ceramics, metal ceramics, resin-based composites, and titanium alloys. Each material has different sintering processes and temperature requirements. You can consult with Brother Furnace about our dental furnaces, including box furnaces and elevator furnaces, to meet your specific needs.





